Table of Contents
What is Surveillance?

Surveillance at its core, refers to the systematic observation, monitoring and recording of individuals, groups or activities.
It involves the collection and analysis of information for the purpose of control, supervision or investigation.
The term “surveillance” originates from the French word “surveiller,” which means “to watch over.”
The scope of it has expanded significantly with advancements in technology, enabling both physical and digital forms of observation.
It encompasses various methods, ranging from overt and visible to covert and discreet monitoring.
It can be carried out by governmental institutions, private entities and even people like you and me, each driven by different motivations and objectives, whether nefarious or justified.
These facts should alarm you.
Not only is the average-joe capable of purchasing monitoring equipment and using it to find vulnerabilities in your daily routine to plan an attack or theft…
Your own government could decide one day you’re a potential person of interest and spy on every single one of your activities directly, even when you’re not doing anything wrong.
Physical Surveillance

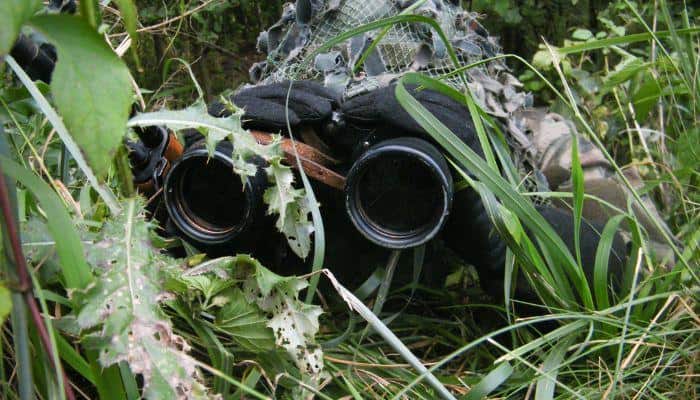
The Human Element
Physical surveillance involves the direct and visual observation of individuals or groups. It can be carried out overtly or covertly, depending on the objectives and circumstances of the operation.
Typically speaking, most ops are covert in nature unless the target needs a little push in the right direction, at which point they become overt and targeted aggression comes into play.
Targeted aggression is the direct intervention of the daily routines or habits of the target. It involves directing annoying or aggravating the target to provoke a certain response, usually something that progresses the investigation or furthers known intelligence.
“Stakeouts” is a common term you’ll see on television or in the movies but it’s absolutely a real practice, the level of sophistication depends on the organization conducting it.
Standard police divisions simply don’t have the training, equipment or budget to surveil people like the CIA would for example.
Some techniques they may use:
- CCTV/Security Cameras: We don’t really have to explain this one, it’s fairly straightforward already but you should know, AI is only making these more and more effective.
- GPS Tracking Capabilities: Nowadays most people make it easy for the watchers by bringing a phone everywhere with them. Unless you’re using a secure OS like GrapheneOS with location and networking off.
- Planted Bugs: Audio/Video remote listening and recording devices can be smaller than a penny and can be attached to nearly anything, some have massive ranges and allow agents to listen from safe distances.
- Biometric Surveillance: Biometric data, such as fingerprints, facial features, iris patterns or gait, is captured and matched against databases to authenticate identities or monitor movement.
- ISR platform tracking: ISR (Intelligence, Surveillance and Reconnaissance) platforms include drones or other aircraft and satellites. These are pretty much exclusive to nation-states and are used primarily for military purposes to provide operators with actionable intel on the ground, but with the amount of privately owned drones on the rise, almost anyone can have amateur eyes in the sky.
Digital Surveillance

The Internet
There are various methods employed to monitor online activities, as well as several kinds of data being collected.
The wide reaching drag-net capabilities of governments, intelligence agencies and even private entities to engage in internet surveillance for purposes like national security, criminal investigations and targeted advertising is highly concerning and when they can’t collect the data, they resort to buying it.
The two main types of data they collect:
- Metadata Collection: The term tends to trip non-techies up, basically it just refers to the information generated during online communications, including sender and recipient details, timestamps, geolocation and communication duration. Covert programs collect and analyze metadata to identify and build patterns of life, analyze relationships and assess potential threats.
- Electronic Intercepts: This involves intercepting and analyzing the content of emails, instant messages, voice calls and other forms of digital communication. Governments and intelligence agencies may or may not obtain legal authorization to monitor specific individuals or groups suspected of criminal activities or threats to national security. This is abused more than most people are aware of, but the good news is you can still do something about it.
Social Media Surveillance
Social media platforms have become fertile ground for surveillance due to the wealth of personal data shared willingly by users.
Social media platforms collect vast amounts of user data, which can be mined and analyzed to create comprehensive profiles. These profiles enable targeted advertising, personalized content delivery and even the prediction of your behaviors and preferences.
This includes real-time monitoring for potential threats, criminal activities and current trends. Automated systems (mostly powered by AI but also combined with real analysts) scan social media posts, keywords and geolocation data to identify patterns.
The Key Players

National Security and Intelligence Agencies
Government organizations such as the national security agency (NSA) or the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) in the US, the Security Service (MI5) in the UK, the Foreign Intelligence Service (SVR) in Russia or Germany’s Bundesnachrichtendienst (BND) are all responsible for gathering intelligence and conducting surveillance operations to protect the nation’s security interests.
These agencies employ a range of techniques, including signals intelligence (SIGINT), human intelligence (HUMINT) and open source intelligence (OSINT).
Law Enforcement Agencies
Law enforcement agencies, at both the national and local levels, use surveillance everyday. They’ve developed specialized techniques to prevent and investigate crimes, gather evidence and ensure public safety.
Just like their counterparts working in national security, they are known to abuse the law frequently and have been caught conducting unauthorized and unwarranted surveillance many times.
Corporate Surveillance
Corporations and businesses engage in corporate espionage for a lot of reasons, including safeguarding assets and gathering intel on what their competition is doing.
Retail stores utilize cameras and monitoring systems to deter shoplifters and looters. The big corporations typically use data analytics and monitoring tools to track employee productivity and behavior too.
Advertising and Data Brokers
Advertising companies and data brokers collect massive amounts of personal information through many different channels, including social media and online purchases.
They take advantage of the same techniques to track consumer behavior, preferences, and demographics. This data is then used for targeted advertising campaigns and the creation of consumer profiles.
The Future of Surveillance

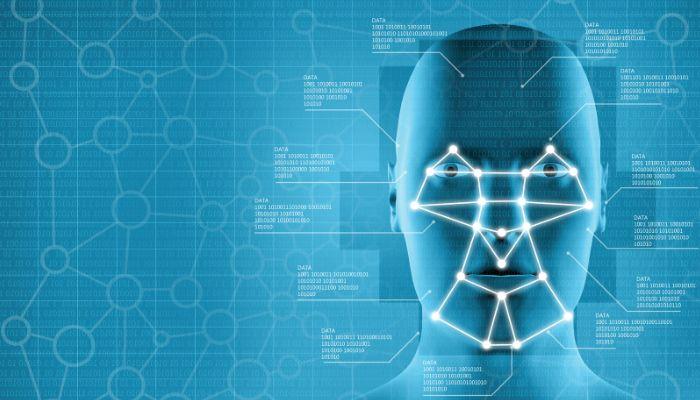
Facial Recognition Technology
Facial recognition technology is a rapidly advancing video tool that analyzes and identifies individuals based on their facial features. It uses algorithms to compare captured images or video footage with databases of known faces.
Biometric Surveillance
Biometric surveillance involves the use of unique physiological or behavioral characteristics to identify you. Data like fingerprints, iris scans, DNA profiles or voice recognition, can be collected and analyzed for identification and tracking.
Big Data and Predictive Policing
This will also transform law enforcement practices. Predictive policing models use historical crime data, social media monitoring and other data streams to forecast where crimes are likely to occur and who is likely to commit them.
The movie Minority Report is starting to look more like our future with each passing day.
Artificial Intelligence and Automation
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation is a booming industry, AI-powered systems can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time to identify patterns and make predictions with increasing accuracy.
Automated surveillance technologies, such as drones and autonomous cameras, can operate independently, enhancing the efficiency and scope of surveillance operations.
What can you do about it?
Now that you know what surveillance is and the potential threat it may pose to you or your loved ones, you can start to do something about.
To be ToughPrey and avoid these kinds of operations being run on you, you’ll need to deploy counter-surveillance techniques. We recommend you check out the following articles:


